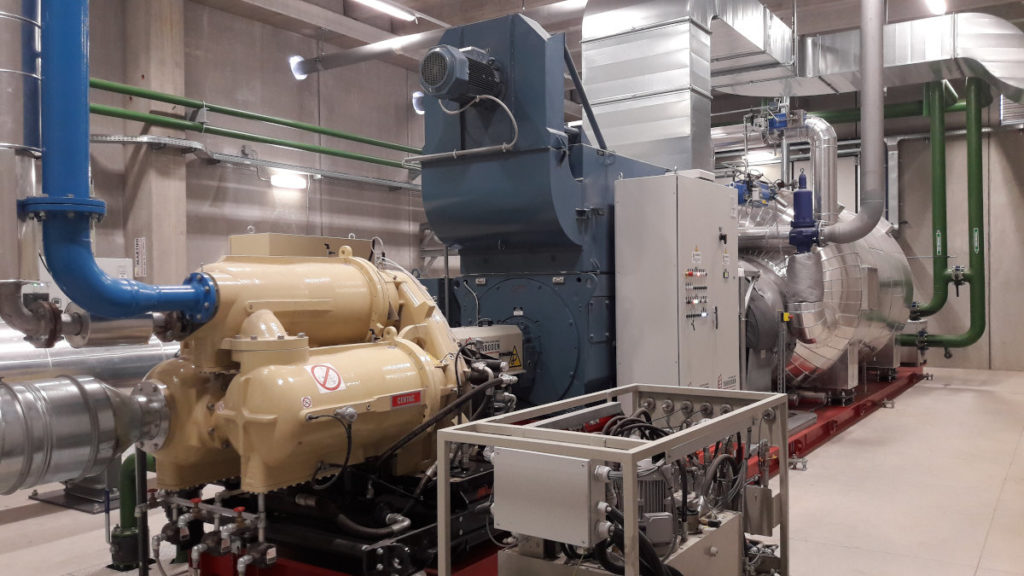
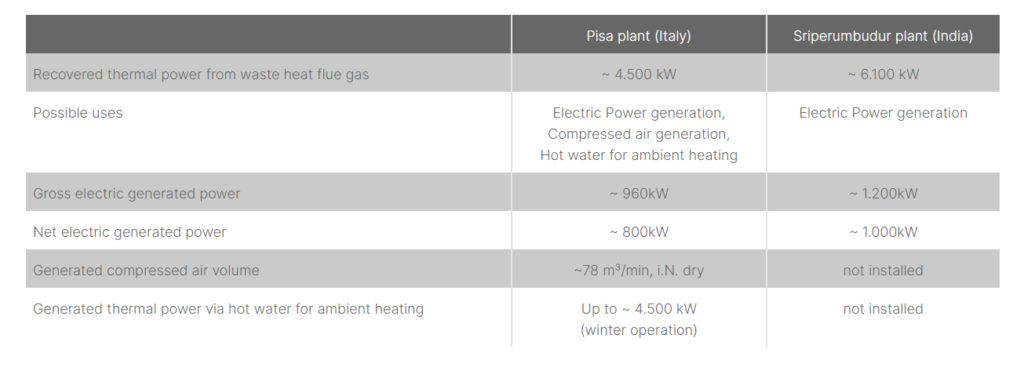
Two plants for waste heat recovery in flat glass production lines of the Saint-Gobain Group at locations in India (Sriperumbudur) and Italy (Pisa) have now been commissioned. In Sriperumbudur, the plant is producing electricity, while in Pisa the production of compressed air and thermal energy for ambient heating are also important factors for the plant. However, both locations have one thing in common: Saint-Gobain can significantly improve energy efficiency in production and save resources with this GEA solution. This is also shown by the characteristic data obtained to date.
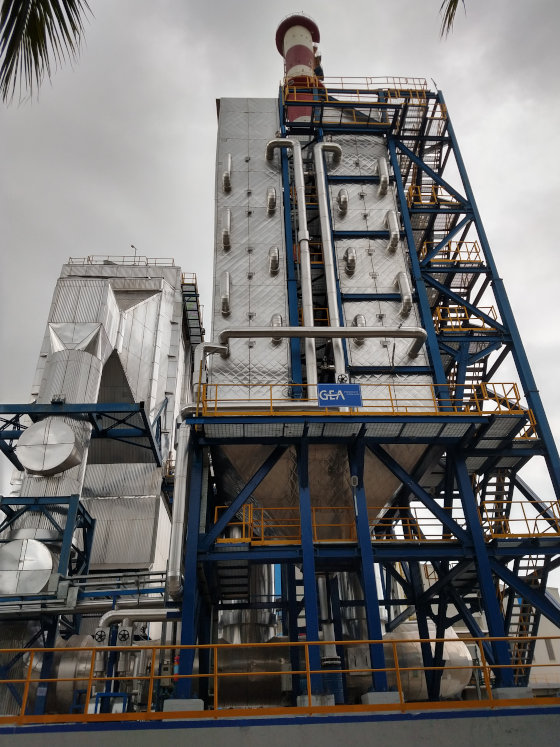

In both plants, the waste heat is extracted from the flue gas in a heat exchanger and transported to an ORC (Organic Rankine Cycle) via a thermal oil circuit at high temperatures around 300°C and with high flexibility. From this, in turn, electrical power is produced. In addition, a compressor is operated at the Pisa plant via the ORC turbine, contributing to the plant’s compressed air supply. In winter, additional flexibility was provided because the heated thermal oil could, at the same time, supply thermal energy to a hot water circuit for ambient heating.
Reduction in CO2 emission and operating cost
After several months of operation, the plants are showing the expected performance. In this way, Gea not only contributes to the sustainability of glass production and the reduction of CO2 emissions but also the reduction of operating costs.
Gea is one of the largest suppliers for the food processing industry and of related industries. The international technology group specializes in machinery, and plants as well as process technology and components. Gea offers sustainable energy solutions for sophisticated production processes in various end-user markets and offers a comprehensive service portfolio. The group generates around 70% of its revenue in the food and beverages sector that enjoys long-term sustainable growth.
The important key data of both waste heat recovery plants are summarized in the table below: